Editor’s note: This post originally appeared on TechNode, an editorial partner of TechCrunch based in China.
From Alibaba to JD, China is not short of e-commerce powerhouses. Although the country’s e-commerce market is highly consolidated, it’s not impossible for startup teams to crack this market as long as they are solving the right problems for the right group of customers.
Chinese social e-commerce platform Pinduoduo just proved this. The Shanghai-based company just went public raising $1.6 billion through a U.S. IPO this week, which stands out as one of the largest deals of the year. Excitement is quickly intensifying surround the company, which claims 195 million monthly users and has managed to become successful within China’s highly competitive e-commerce market inside just three years.
What is Pinduoduo and what has it done right?
Like Alibaba’s Taobao and rival JD.com, Pinduoduo is an e-commerce platform that offers a wide range of products from daily groceries to home appliances. Pinduoduo’s twist lies in its integration of social components into the traditional online shopping process, which the company describes as the “team purchase” model.
By sharing Pinduoduo’s product information on social networks such as WeChat and QQ, users can invite their contacts to form a shopping team to get a lower price for their purchase. The mechanism keeps the users motivated and better hooked for a more interactive and dynamic shopping experience. Coupled with other incentives such as cash, coupon, lottery and free products, Pinduoduo manages to acquire users at a very low cost. Combined with the extra satisfaction of scoring a good deal with your friends as a team, Pinduoduo soon became a viral sensation in China.
Extremely low prices are another compelling attraction of Pinduoduo. The discount is usually up to 90 percent, including everything from RMB 10 ($1.50) bed sheets to RMB 1,000 ($150) PCs. But the bestsellers are daily items at unbelievable low prices. More than 6.4 million units of tissue paper were sold at RMB 12.9 ($1.90) for 10 boxes and 4.8 million umbrellas were purchased at RMB 10.3 ($1.51) apiece.
The company’s bulk-selling model easily creates huge orders for the sellers and leaves them more room to cut prices. At the same time, Pinduoduo’s app is designed to facilitate this, an expert explained to local media: “Alibaba Taobao’s interface is search-based and centered on multiple product displays, while Pinduoduo’s is more similar to a news feed and thus gives more exposure to a single product and easy to create “爆款” [baokuan, meaning viral items]. Taobao has more products listed, but Pinduoduo put its focus on fewer bestsellers that attract more buyers.”

Pinduoduo (l) and Taobao (r) interfaces
Pinduoduo’s C2B model allows it to ship directly from the manufacturers eliminates layers of distributors, not only reduces the price tag for buyers but also raises the profit of manufacturers. This approach is particularly effective for the sales of perishable agricultural and fresh products, where the speed for matching supply and demand is critical.
Lesser-known brands were chosen over famous brands to erase any premium that comes from branding. Additionally, the costs for advertising and marketing are also lowered through user sharing to social media. The approach is both cost-saving and effective. Through social sharing, users are sending the product information precisely to friends and groups that may have similar income and consumption preferences. Viral marketing is a more clever way to build the identity of all the lesser-known brands on its platform. Financially, the platform could even out part of discounts with less marketing budgets.
Price and social features are not only the only path to Pinduoduo’s meteoric rise, and spotting the right user profile is the last piece to the puzzle.
Operation director of Chinese mobile e-commerce platform Chuchujie, Yang Lin shot to the core of the problem in an interview with local media: “Taobao has over 500 million users while WeChat has over 1 billion, the gigantic missing group between two of China’s giant apps is distributed in third- or lower-tier cities, mostly senior citizens. This group, which only recently came online and depends on the ubiquitous WeChat as the chief source of information, is the target users of Pinduoduo.”
Data from research institute Jiguang shows that users from third- and lower-tier cities account for around 65 percent of Pinduoduo’s total user base, while JD’s users in first plus second-tier cities and the rest of China were half-and-half. Additionally, females account for 70 percent of Pinduoduo’s user base. They are responsible for family purchases and more price sensitive. This guarantees more active sharing and purchases.
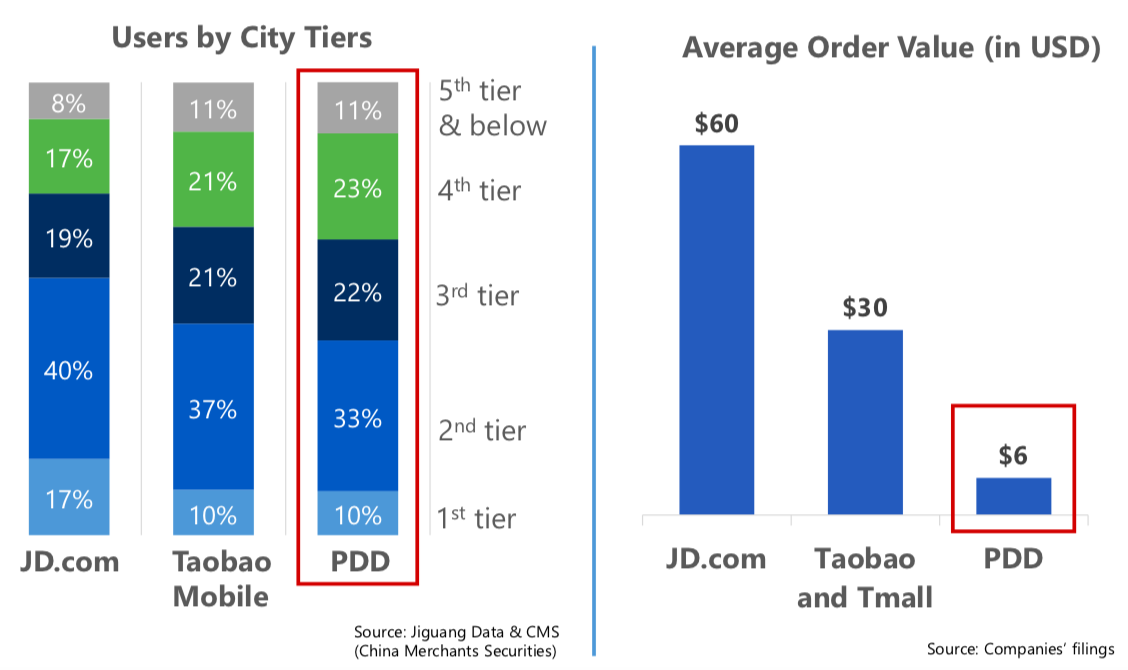
User demographics and average order value of JD, Taobao, and PDD (Image credit: GGV)
Consumption upgrade, a trend in which affluent Chinese customers are increasingly willing to pay for quality, has dominated China’s e-commerce industry in the past few years. Taobao and JD’s globalization initiatives to bring overseas quality products, the boom of cross-border e-commerce sites like Red and NetEase Yanxuan and Kaola are all based on the consumption-upgrading backdrop.
But the growth of Pinduoduo has sparked an argument focusing on whether the platform represents consumption downgrading. Maybe consumption upgrading or degrading isn’t the key problem. It is just one more piece of evidence for how big and segmented the Chinese market can be. Rising income may give part of Chinese urban citizens the freedom to vote for quality, but RMB 1 difference in price tag may be enough of an incentive for their countryside counterparts, who have been more neglected by e-commerce so far.
Cost performance is still the most important factor to consider for consumers. A higher price tag does not necessarily represent the better quality or vice versa. The huge potential in this often-overlooked market is luring more competitors. Taobao launched Taobao Tejia, a dedicated app for China’s low-end users.
Pinduoduo didn’t invent the social e-commerce model. Groupon pioneered the group-buying concept years ago. But it is succeeding thanks to a new ecosystem consisting of super app WeChat, mobile payment infrastructure, and mobile-first users.
Pinduoduo’s history and major milestones
Founded in September 2015, Pinduoduo is the fourth startup of Colin Huang, an ex-Googler who once worked on early search algorithms for e-commerce. His previous startups include consumer electronics e-commerce site Ouku.com, Leqi, e-commerce platform marketing agent service and a WeChat-based role-playing game company.
With experiences in both e-commerce and gaming, Huang founded Pinduoduo with a vision to combine the secret success recipe of both Alibaba and Tencent, the two Chinese internet giants known for their e-commerce and gaming /social dominance respectively. “They don’t really understand how the other makes money,” Huang said to Bloomberg.
Huang seems to be right about how the two industries can work together. Pinduoduo’s annual GMV (gross merchandise volume) surpassed RMB100 billion ($14.7 billion) in 2017, that’s around two years since its inception. To hit the same milestone, Taobao took five years, VIP.com took eight years and JD ten years. Pinduoduo now claims more than 343.6 million active buyers with an annual GMV of RMB 262.1 billion, or $38.5 billion.
A huge turning point occurred in the third quarter of 2017 when the weekly active rate, penetration rate, and open rate of the Pinduoduo app all surpassed those of JD. Compared to the previous year, it reaches up to 1,000 percent year on year growth according to data from Jiguang.

Image credit: GGV Capital
Steep growth trajectory lured financial backings. In 2015, Huang launched Pinhaohuo, a social commerce platform for fruits, with the team from his second startup Leqi. His gaming startup incubated Pinduoduo.
Four months after Pinduoduo received undisclosed A round from IDG and Lightspeed China in March 2016, the company secured over $110 million in Series B financing four months later from Baoyan Partners, New Horizon Capital, Tencent, and others. In April 2018, Pinduoduo completed a new round of financing raising $3 billion at a valuation of nearly $15 billion. Given Pinduoduo’s WeChat-based ecosystem, Tencent joined the round as a returning investor.
Given the history between Pinduoduo and Pinhaohuo, then of the two largest players in the social e-commerce sector, the two companies merged to form one dominator.
Another counterfeit heaven in China?
“If you close your eyes and visualize the next stage for Pinduoduo, it would be a combination of ‘Costco’ and ‘Disneyland’, driven by a distributed network of intelligence agents,” Huang wrote in the IPO prospectus. Huang’s comparison was thus interpreted as a combination of “value for money” and entertainment, but many are questioning whether or to what degree Pinduoduo can live up to the founder’s expectation.
Although Pinduoduo claims to have several channels to lower product prices, increasing product quality and counterfeit complaints still raise concerns for a possible low-cost and low-quality association. The percentage of complains on Pinduoduo is 17.87 percent, and the user satisfaction rating is only 1 star, according to the 2017 National User Satisfaction Survey of Major E-commerce Platforms released by the China E-Commerce Research Center. Complaints mainly target at the problems of poor quality, slow delivery, misleading ads, etc.
In addition to mounting domestic complaints, the Chinese shopping app was hit by a trademark infringement lawsuit in the US, shortly after filing for a US IPO. Alongside Alibaba and JD’s efforts to remove fake goods on their platforms, fake goods are flooding to emerging e-commerce platforms like Pinduoduo and Weishang, according to Alibaba.
As Pinduoduo gets into life as a public company, the firm is following the e-commerce giants in cleaning up the platform. According to the company’s annual consumer rights protection report for 2017, it has taken down 10.7 million problematic listings, blocked 40 million suspicious external links, representing 95 percent of the fake good sellers from the platform. The company set up an RMB 150 million ($22 million) fund to deal with after-sales disputes.
But tightening regulation is causing more friction between Pinduoduo and its merchants on the platform. In June, fourteen store owners who sell products on Pinduoduo protested under the company’s office building claiming that Pinduoduo conducted improper product-quality checks which damaged the owners’ rights. Company founder Huang insisted Pinduoduo’s decision and punishment of the owners is just and fair.
Many also questioned the validity of entertaining features in Pinduoduo’s value proposition. “We have observed that a few users find shopping on Pinduoduo to be very entertaining, which is attributable to its extremely low pricing and interaction among Weixin users,” according to research institute 86 Research.
IPO and beyond
Pinduoduo went public on NASDAQ market on July 26 and raised more than $1.6 billion with a valuation of $60 billion. However, shareholders should still be concerned about the company’s fundamentals
Financially, the company is still in the red. Pinduoduo suffered a net loss of RMB 292 million ($43 million) and RMB 525.1 million ($77 million) in 2016 and 2017, respectively. Its net losses reached RMB 201 million ($30 million) in the first quarter of this year. The net loss is expected to be widened, mainly attributable to investments in branding and ads. Over 88.4 percent of Pinduoduo’s RMB 1.2 billion ($180 million) Q1 revenue was spent on marketing. This could be translated as a sign of difficult traffic acquisition.
The most typical Pinduoduo users are price sensitive women that reside in low tier cities. Merchants are selling at a low price to appeal to this group. But how to maintain these users and its growth momentum is a big challenge for Pinduoduo now given rising product quality complaints.
“The retention rate is a big challenge of Pinduoduo, implying potential GMV slow down. Pinduoduo will have difficulty in upgrading to a marketplace of premium products because of its user demographics and brand image,” according to 86 Research.
from TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2mOHFI6
EmoticonEmoticon